Before you explain a grade to a student, a parent, or even to yourself, you have to confront a deeper question. What does that grade actually represent?
When you ask how to justify student grading, you are not simply asking how to defend a number in a grade book. You are asking whether that number carries meaning. A grade should communicate something important about student learning. If it does not, it becomes a label without substance.
Grade validity is central here. Grade validity refers to the degree to which a grade accurately reflects mastery of the subject matter. If the final grade includes elements unrelated to content mastery, such as attendance or behavior, its meaning begins to blur. When grading systems mix achievement with compliance, the message becomes unclear. Students are left guessing what the grade truly measures.
Creating a meaningful grade is difficult. It requires more than tallying points across individual assignments. It demands a clear framework that defines what is being measured and why. That framework must align with learning goals and specify how performance demonstrates achievement.
When your grading systems are anchored in explicit criteria, justification becomes straightforward. The grade’s meaning is visible within the structure itself. Without that structure, the final grade risks becoming a vague summary rather than a precise reflection of what a student actually learned.
Why Must Grades Reflect Mastery Rather Than Compliance?
Grades lose credibility when they measure the wrong things. If a course grade blends punctuality, attendance, extra credit, and behavior into the same calculation as demonstrated understanding, the signal becomes distorted.
A student may earn a high total grade through compliance while struggling with content mastery. Another may understand the material deeply yet receive a lower score because of late submissions or uneven participation. In both cases, the grade fails to communicate clearly.
Grades become invalid when behavior is folded into academic evaluation without distinction. That does not mean behavior is irrelevant to the class environment. It simply means it should not obscure what you are actually trying to measure.
When grading criteria include irrelevant factors, accuracy declines. When you leave out those factors and focus on evidence tied directly to learning goals, precision improves.
Criterion-referenced assessment provides structure for this clarity. Instead of grading on a curve or comparing students to one another, you evaluate student work against defined standards. Each assignment becomes an opportunity to demonstrate particular skills aligned with learning outcomes. The focus shifts from competition to demonstration.
The assessment must align with the intended skill. If the learning goal involves analytical writing, the grading criteria should measure analytical writing.
If the goal involves problem solving in mathematics, the evaluation should reflect that specific competence. Individual assignments contribute to the total grade only insofar as they measure those defined objectives.
When grades reflect mastery rather than compliance, they communicate something reliable. They show what a student knows and can do. That clarity strengthens both fairness and trust in the grading process.
How Do Clear Criteria Protect Grade Validity?
Once you decide that grades must reflect mastery, the next safeguard is clarity. Vague expectations weaken grade validity faster than almost anything else. When students are unsure what counts, evaluation begins to feel arbitrary. When instructors rely on instinct instead of defined grading criteria, consistency erodes.
Clear criteria do more than organize a rubric. They transform grades from static labels into tools for growth. If an assignment measures analytical reasoning, the criteria should describe what analytical reasoning looks like at different performance levels.
If the goal is problem solving, the standards must outline what successful problem solving demonstrates. Explicit criteria measure the intended teaching goals. Without that alignment, the grade becomes detached from the learning process it is meant to represent.
Using detailed rubrics reduces ambiguity for both students and instructors. Students understand how their work will be evaluated. Instructors anchor decisions in documented expectations rather than momentary impressions. Over time, this structure strengthens trust in the assessment process.
Criteria also serve as a snapshot of achievement. They capture how well a student has met clear learning goals at a specific point. In standards based grading, this alignment becomes even more visible.
Instead of accumulating points, students demonstrate proficiency on defined learning outcomes. The grade reflects demonstrated understanding rather than accumulated credit.
Effective criteria should be :
- Align directly with learning outcomes and course objectives
- Use measurable language that describes observable performance
- Exclude irrelevant factors unrelated to content mastery
- Be communicated from the very first day of class
When grading criteria are transparent and stable, grade validity becomes easier to defend. The structure itself justifies the outcome.
What Role Do Rubrics and Exemplars Play in Justification?
Clear grading criteria set the foundation, but rubrics make that foundation visible. A well-designed rubric breaks an assignment into defined components, each tied directly to learning goals.
In a criterion-referenced assessment process, student work is evaluated against established standards rather than against other students. That distinction matters. It shifts the conversation from comparison to evidence.
Rubrics serve another function that is often overlooked. They protect both instructors and students during grade disputes. When feedback connects directly to specific criteria, justification becomes less personal and more procedural. You are not defending an opinion. You are referencing documented expectations.
Student-friendly rubrics further reduce ambiguity. When performance levels are described in clear language rather than abstract terms, students understand what content mastery looks like. Exemplars deepen that understanding.
By analyzing examples of high-quality and low-quality work, students see how criteria apply in practice. Annotated examples reinforce standards by showing precisely where expectations are met or missed.
The difference between weak and strong justification becomes visible when structure is compared directly:
| Weak Justification | Strong Justification |
|---|---|
| Vague comments detached from criteria | Rubric-linked feedback tied to specific standards |
| No exemplars provided | Annotated examples illustrating expectations |
| Curve grading based on relative ranking | Criterion-referenced evaluation against fixed criteria |
| Mixed behavior and academic skill categories | Skill-based categories focused on mastery |
| Criteria explained only after grades are released | Criteria shared early in the semester |
When rubrics and exemplars are integrated into grading practices, justification shifts from explanation to demonstration. The structure itself carries the evidence.
How Can Involving Students Strengthen Grade Justification?

Justification becomes stronger when students are not passive recipients of grades but active participants in the assessment process. When students self assess their work against clearly defined criteria, the grade becomes part of the learning process rather than a final verdict.
Student-reflection based grading systems invite students to assign a provisional grade to their own work, grounded in reflection about what they accomplished and where they fell short. This practice enhances understanding of the learning process.
Instead of focusing only on the final grade, students examine how well they demonstrated particular skills and how their work aligns with learning goals.
Peer review also plays a role. When students evaluate exemplars using the rubric, they see how criteria operate in practice. They recognize patterns of strength and weakness. That analytical exercise sharpens their awareness before submitting their own assignment.
Co-creating elements of the rubric can further deepen ownership. When students contribute to defining expectations, they are more likely to internalize them.
Involving students does not weaken standards. It clarifies them.
You can involve students by:
- Implementing self-grading wrappers that require reflection before submission
- Analyzing exemplar work in small groups using the rubric
- Encouraging reflection on strengths and areas for revision
- Co-creating selected rubric criteria to clarify expectations
- Setting personal learning goals aligned with course objectives
When students engage directly with grading criteria, justification becomes shared understanding. The grade reflects not only evaluation, but awareness.
When Do Alternative Grading Models Improve Justification?
Alternative grading models improve justification when the traditional point-accumulation approach no longer explains what a student actually knows. If your total grade is built from scattered percentages, extra credit, participation points, and curve adjustments, the final number can blur more than it clarifies. Justification weakens when explanation requires too many footnotes.
Specifications grading offers one response. In this model, assignments are evaluated against clearly defined competency standards. Work either meets the specification or it does not. The criteria are explicit, measurable, and tied to learning goals.
Students know in advance what is required to demonstrate achievement. There is less ambiguity, and therefore less dispute.
Standards based grading takes a similar path. Instead of reporting a single blended percentage, it reports performance on specific learning targets. You do not simply say a student earned an 87 percent. You indicate whether they have mastered particular skills.
This strengthens justification because the grade reflects mastery of defined outcomes rather than accumulated points.
Mastery-based grading goes further by allowing multiple opportunities to demonstrate understanding. A low score is not treated as a final judgment but as information. Reassessment supports mastery. Students can revisit material, apply feedback, and show improvement.
When multiple opportunities exist, the final grade represents the highest level of demonstrated achievement, not the first attempt.
Many mastery systems use a 4-point mastery scale, where each level corresponds to defined performance standards. This structure simplifies interpretation.
It also aligns formative assessments with summative ones. When each reassessment is anchored to the same criteria, justification becomes procedural rather than personal.
Alternative grading models improve justification when they align evidence with learning goals, allow growth, and clarify what mastery truly means. The grade becomes a conclusion drawn from defined standards, not a composite impression accumulated over time.
How Does Transparency Protect Against Grade Disputes?

Disputes rarely begin with numbers. They begin with uncertainty. When students do not understand how grades are calculated, or what a final grade truly represents, doubt grows. Transparency interrupts that cycle.
If you want to justify student grading, clarity must begin on the first day of class. Grading policies should be outlined in the syllabus in plain language. Students should understand how individual assignments contribute to the course grade, how report grades are calculated during each marking period, and how the reporting system translates performance into the grade book. Ambiguity invites challenge. Clear structure discourages it.
Explaining your grading philosophy early also matters. When students know why particular criteria exist and how learning goals shape the grading process, they are more likely to perceive the system as fair. A grade should not surprise them. It should confirm what the criteria already suggested.
A grade-challenge policy strengthens transparency further. Many instructors use a 24-hour cool-off period before students can contest a grade.
This pause reduces reactive emotion. Requiring a written explanation tied to rubric criteria shifts the conversation from frustration to evidence. The focus returns to standards, not opinion.
Transparent systems include:
- Clear syllabus grading policies communicated from the beginning
- Defined grade weightings for each assignment and assessment category
- Published rubrics linked to learning objectives
- A written appeal process outlining timelines and expectations
When transparency is built into the grading system, disputes become discussions grounded in criteria. The grade’s meaning is visible. And when meaning is visible, justification becomes far less defensive and far more procedural.
What Evidence-Based Practices Reduce Bias in Justification?
Bias rarely announces itself. It moves quietly, often beneath awareness, shaping impressions before criteria have a chance to speak. If you are serious about equitable grading, your justification must be grounded in structures that limit subjectivity, not just good intentions.
Anonymous grading is one of the simplest and most effective practices. By removing student names from assignments, you reduce the influence of prior impressions, participation patterns, or personal familiarity.
Research shows that even well-intentioned teachers and instructors can carry unconscious biases that affect evaluation. When identifying details are hidden, the assessment process becomes more tightly aligned with the work itself. The grade reflects evidence, not perception.
Horizontal grading adds another layer of consistency. Instead of grading one student’s entire assignment before moving to the next, you grade the same question or task for the entire class at once. This method stabilizes expectations.
Your internal standard remains steady because you are applying the same criteria repeatedly in a short window of time. Drift, fatigue, and subtle recalibration are less likely to distort outcomes.
Grade-norming sessions are especially important when multiple graders or teaching assistants are involved. In these sessions, graders evaluate sample responses together, compare judgments, and reconcile differences before assessing the full set of submissions.
This alignment process clarifies how rubrics should be interpreted. It prevents one instructor from scoring generously while another applies stricter standards.
Standardized rubrics underpin all of these practices. Clear, criterion-referenced tools minimize subjective bias by defining what constitutes proficiency at each performance level. When expectations are explicit, justification becomes easier to articulate. You can point to specific evidence in the student work and link it directly to defined standards.
Evidence-based practices do not eliminate human judgment. They discipline it. And when judgment is disciplined through structure, justification becomes more equitable, defensible, and aligned with the learning goals of the class environment.
How Can Feedback Strengthen the Case for a Grade?
A grade without feedback feels abrupt. A grade with feedback becomes evidence.
If you are thinking about how to justify student grading, feedback is not an accessory. It is documentation. It shows how the assessment process connects to student learning, and it explains why a particular course grade or assignment score was earned.
When students receive feedback that is timely and specific, they see how performance aligns with defined criteria. When feedback is delayed or vague, the grade feels arbitrary.
Timely feedback matters because momentum matters. When students receive feedback soon after submission, they can connect it directly to their thinking. Formative assessments are especially powerful in this regard.
They allow students to correct misunderstandings before the final grade is assigned. The grade then reflects growth, not just initial performance.
Action-oriented feedback supports progress. Instead of announcing that something is wrong, it identifies gaps and indicates how to close them. This transforms grading from a final judgment into a growth conversation. Students are more likely to engage with the learning process when they understand what improvement requires.
Feedback also protects grade validity. When comments are anchored in rubric categories and learning goals, they demonstrate that evaluation is evidence-based. If a student questions a score, you can point to documented feedback that connects the outcome to specific criteria.
Justifiable feedback should:
- Reference the relevant rubric category or grading criteria
- Identify specific gaps in understanding or execution
- Suggest concrete revisions or next steps
- Align clearly with stated learning goals
When feedback is meaningful, the grade no longer stands alone. It is supported by a record of guidance, revision, and measurable progress. Justification then rests not on authority, but on documented learning.
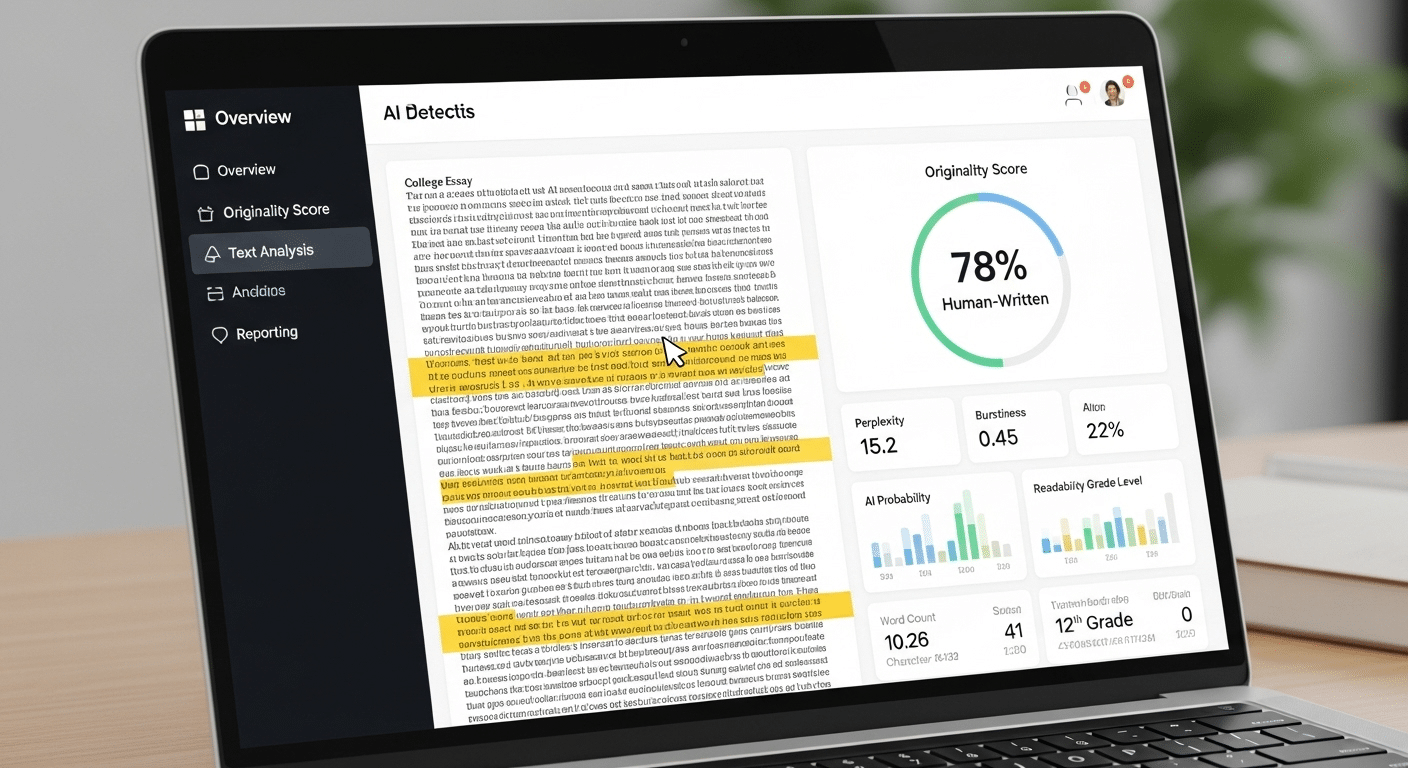
How Does TrustEd Reinforce the Justification of Student Grades?
Justification depends on one assumption that is easy to overlook. The work being graded must actually belong to the student.
In an era where generative AI can produce essays, problem solutions, and even reflective writing in seconds, that assumption no longer holds automatically. If authorship is uncertain, grade validity weakens. You cannot confidently explain how student work demonstrates mastery if you are unsure who created it. The assessment process becomes vulnerable, and grading systems risk losing credibility.
TrustEd addresses this challenge without turning the classroom into a surveillance environment. Its purpose is not punitive. It is protective. By verifying authorship and identifying potential AI misuse responsibly, TrustEd strengthens equitable grading. It allows you to apply grading criteria to authentic student work, not outsourced responses.
When authenticity is preserved, justification becomes defensible again. You can point to evidence in the assignment, align it with learning goals, and explain the final grade with confidence. Without that foundation, even the most detailed rubric struggles to hold.
Integrity is not an abstract principle. It is the condition that makes evaluation meaningful. When student work is verified, the grade communicates what it should communicate. Achievement. Mastery. Growth. In that sense, TrustEd does not replace sound grading practices. It reinforces them, ensuring that justification rests on genuine evidence rather than assumption.
Conclusion
At its core, a grade is a signal. Not a reward. Not a punishment. A signal.
If you are serious about how to justify student grading, you must decide what that signal means. A grade should communicate one clear message about student achievement. It should indicate the level of mastery demonstrated against defined learning goals. Nothing more, nothing less. When irrelevant factors creep in, when criteria are unclear, when authenticity is uncertain, the signal distorts.
Valid measurement depends on alignment. The assessment must measure the intended skills. The grading criteria must reflect those goals. The final grade must accurately reflect the evidence collected across the learning process. When transparency, consistency, and integrity work together, the grade becomes credible. It tells students where they stand and what growth remains possible.
Justification is not about defending a number. It is about ensuring that number accurately represents demonstrated achievement. It is about preserving trust within the class environment.
If you want to strengthen that clarity and protect grade validity in the age of AI, explore how TrustEd can help reinforce authentic, transparent evaluation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What makes a grade valid?
A grade is valid when it accurately reflects a student’s mastery of clearly defined learning goals. It must be based on relevant evidence, aligned assessments, and consistent grading criteria. When irrelevant factors such as behavior or attendance distort the result, grade validity weakens.
2. How do you justify a grade to a student?
You justify a grade by connecting it directly to documented criteria and specific evidence in the student’s work. Clear rubrics, timely feedback, and transparent grading policies allow you to explain how the final grade was determined within the assessment process.
3. Should participation count toward grades?
Participation can be assessed, but it should not distort academic mastery. If included, it must measure clearly defined skills, such as discussion analysis or collaborative problem solving. Mixing behavior with content mastery can undermine the grade’s meaning and validity.
4. What is mastery-based grading?
Mastery-based grading focuses on whether students demonstrate specific measurable skills and learning outcomes. It often allows multiple opportunities to show improvement. The emphasis shifts from accumulating points to demonstrating content mastery through aligned assessments.
5. How can self-assessment improve grading fairness?
When students self assess using the rubric, they better understand grading criteria and their own learning progress. Reflection promotes ownership and transparency. It also clarifies expectations before final evaluation, strengthening equitable grading practices.
6. How does TrustEd support grade integrity?
TrustEd verifies authorship and identifies potential AI misuse before grading occurs. This ensures grading systems evaluate authentic student work. By protecting academic integrity, it reinforces grade validity and supports fair, transparent evaluation across the entire class.