Somewhere between the third essay of the night and the cold coffee on your desk, it becomes obvious. This pace doesn’t scale. Teachers spend hours grading essays, often after the school day ends, weekends slipping away line by line. Essay grading is easily one of the most time-consuming parts of teaching, not because it lacks value, but because it demands focus, care, and consistency every single time.
Lately, AI grading tools have entered the conversation, promising speed, consistency, and timely feedback for student writing. Tempting, yes. But also unsettling.
Questions surface quickly. Is it fair? Will bias creep in? What happens to academic integrity? And most importantly, where does human judgment fit?
In this article, you’ll see how to grade student essays with AI in a way that actually saves time without flattening quality. We’ll look at how it works, where it helps, where it falls short, and how to stay firmly in control of the grading experience.
What Does It Mean to Grade Student Essays With AI?
Grading student essays with AI doesn’t mean handing the keys over to a machine and walking away. That fear lingers, understandably. In practice, AI essay grading works very differently.
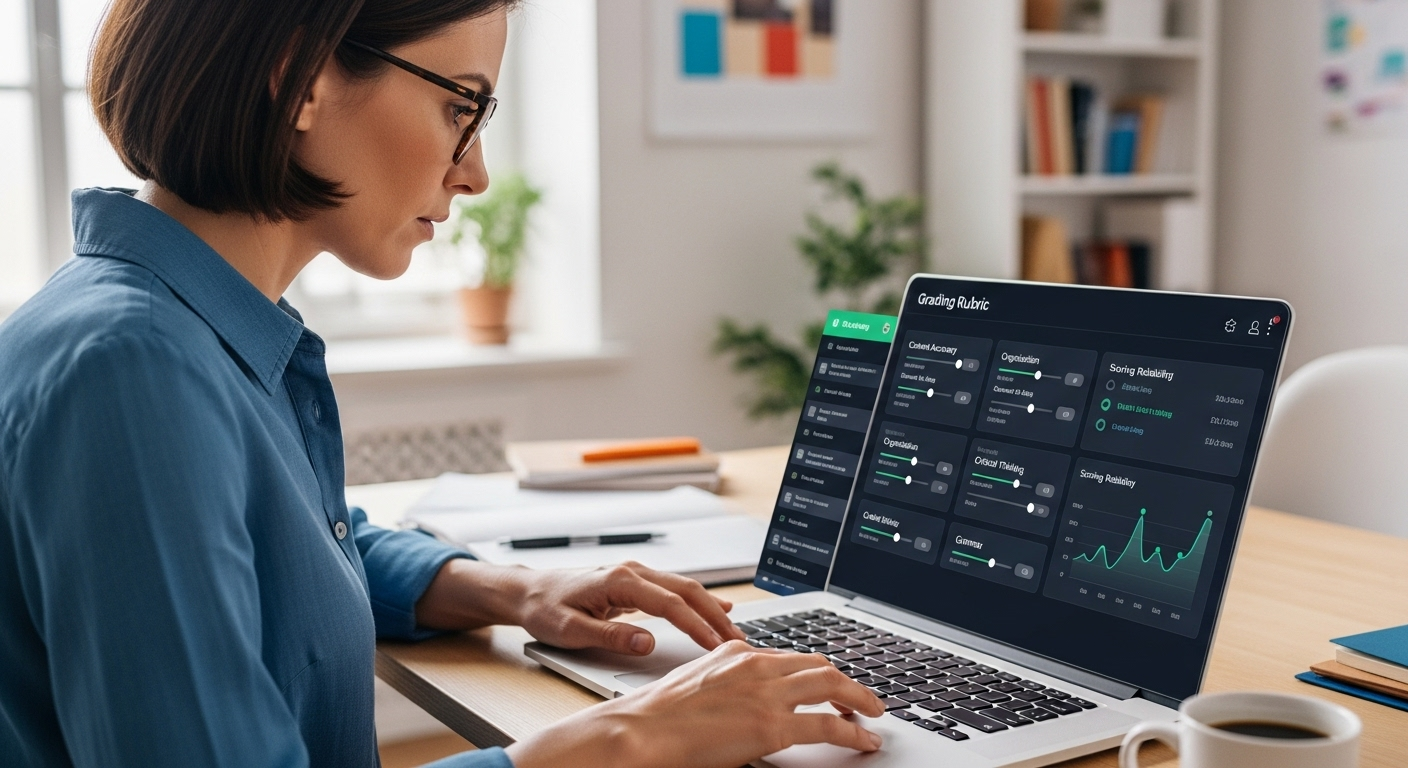
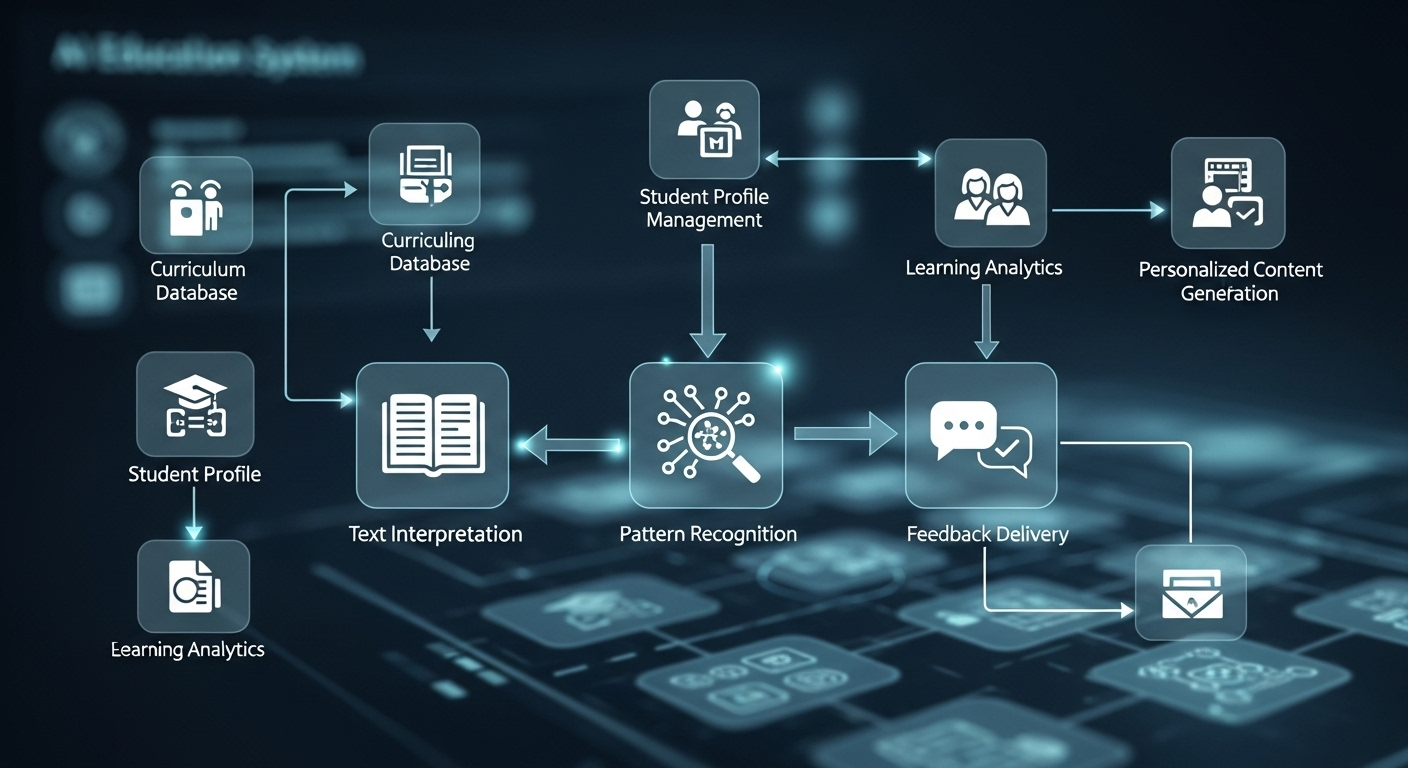
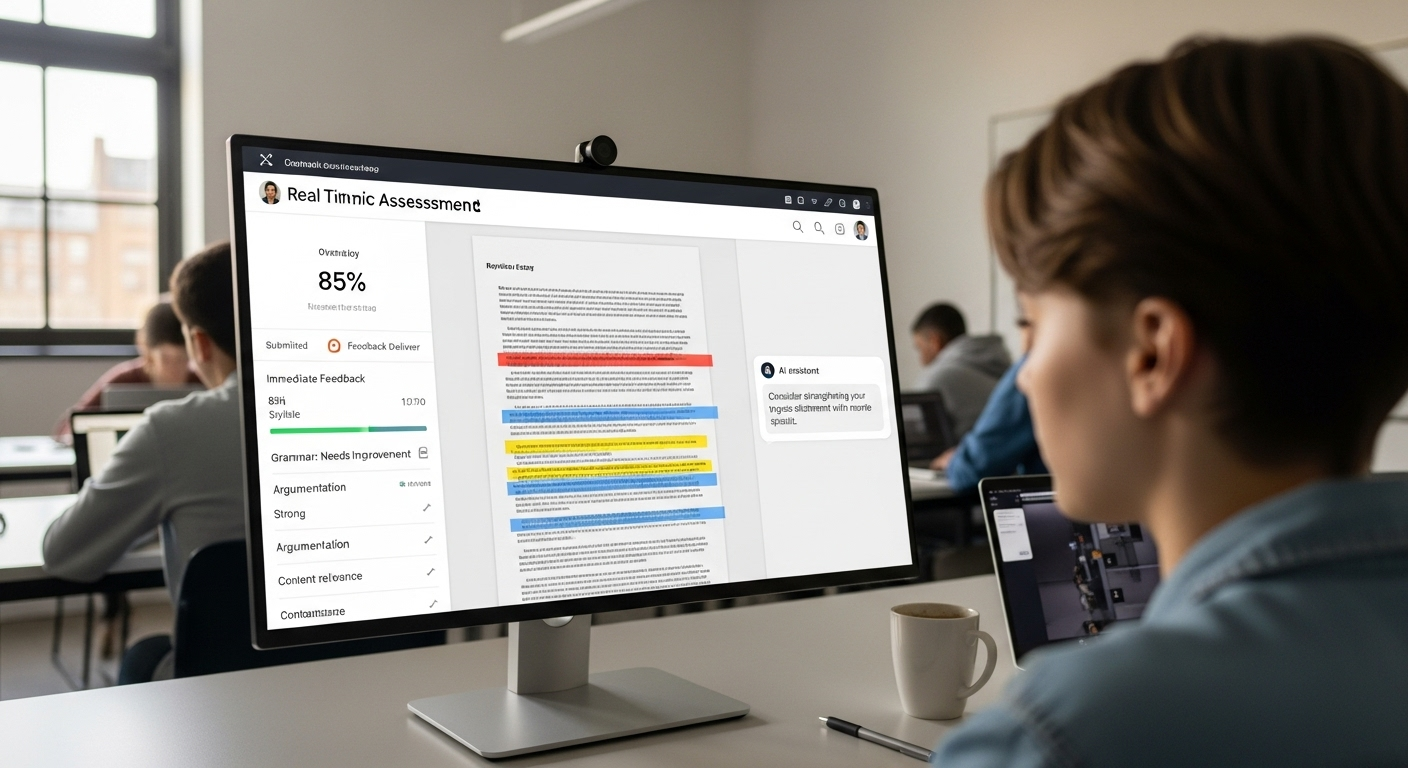
An AI essay grader uses advanced algorithms, natural language processing, and machine learning to analyze written work. It looks at structure, grammar, clarity, coherence, and how closely a piece of writing aligns with a grading rubric. Some tools also surface patterns across an entire class, helping you spot common strengths or gaps faster than a human eye ever could.
What it doesn’t do, at least not responsibly, is replace you. AI grading is not fully automated grading where feedback and final scores appear without oversight.
In 2026, best practice is clear: AI works best as a first-pass assistant. It handles the repeatable, time-heavy parts of essay grading, while you focus on judgment, nuance, originality, and intent.
When using AI to grade, teachers retain full control. You review suggestions. You adjust feedback. You assign the final grade. Human grading remains the authority. AI simply helps you get there faster, with more consistency, and without spending every evening buried in student essays.
How Do AI Essay Graders Actually Work Behind the Scenes?
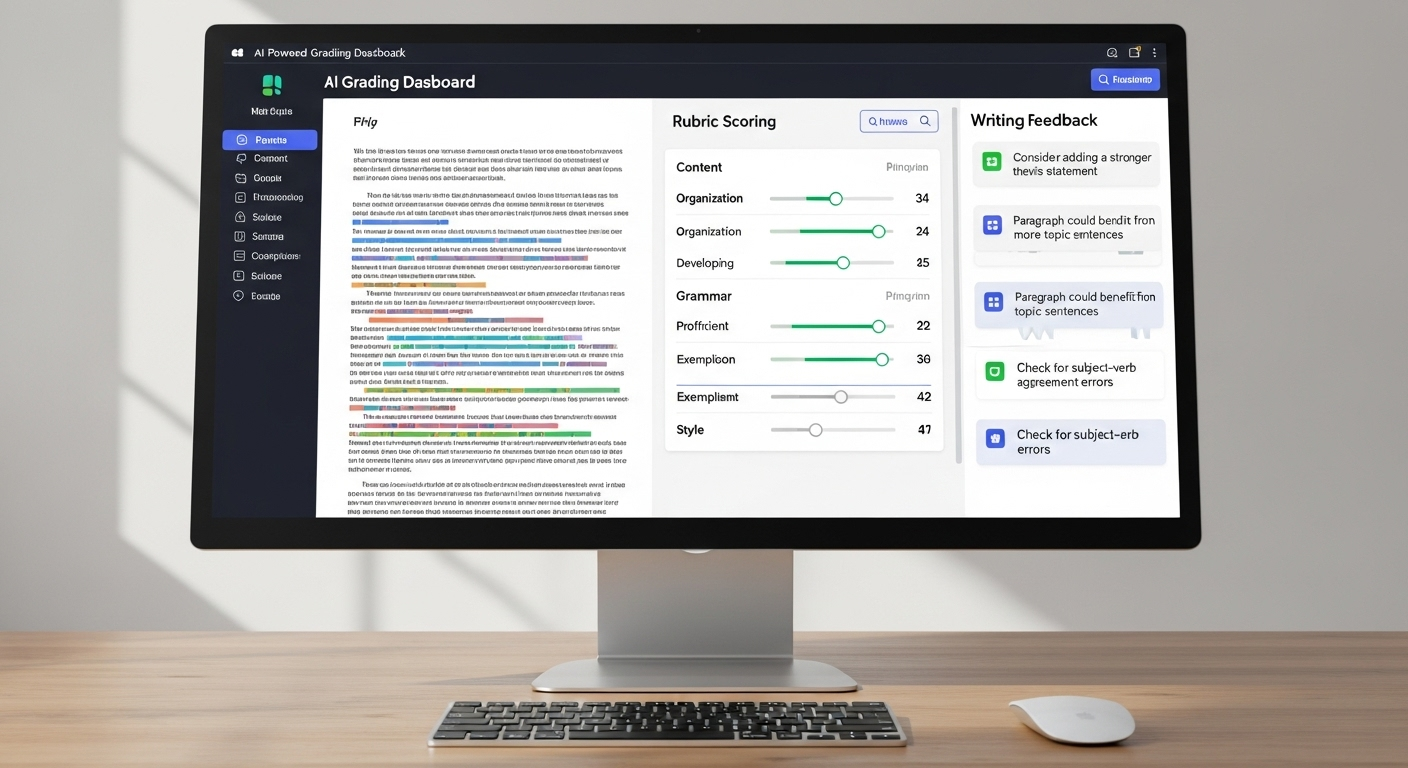
At first glance, AI essay grading can feel a bit like a black box. You upload student submissions, and out comes feedback. But under the hood, the process is far more methodical and, frankly, less mysterious than it sounds.
AI models analyze student submissions using natural language processing, breaking written work into patterns that machines can evaluate consistently. Instead of “reading” like a human, the system examines sentence structure, cohesion, tone, and grammar at scale. Each essay is then evaluated against an uploaded grading rubric, so the criteria guiding feedback are yours, not the AI’s imagination.
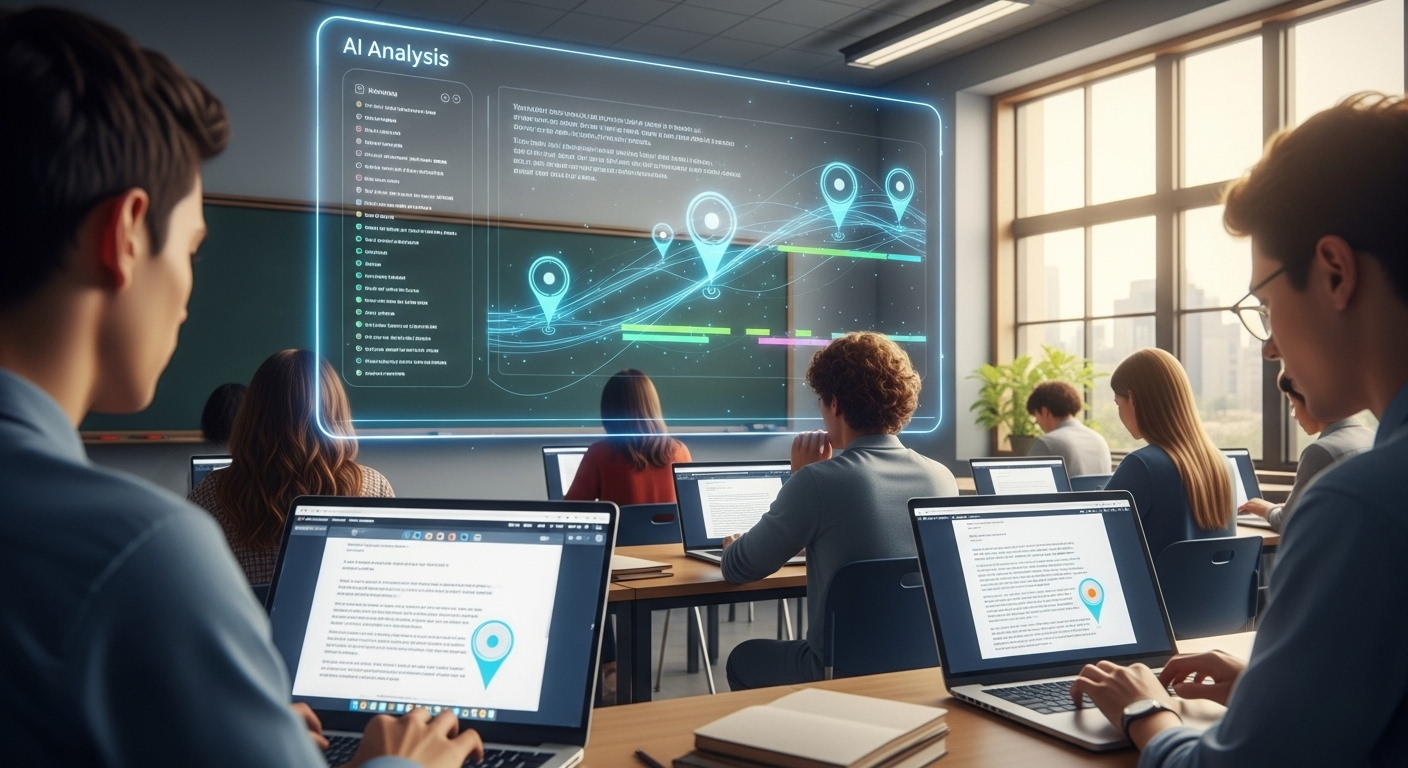
What makes AI grading especially useful is its ability to compare patterns across an entire class. If multiple students struggle with thesis clarity or paragraph flow, the system notices.
Importantly, AI graders don’t make irreversible decisions. They flag potential issues, surface suggestions, and highlight inconsistencies, leaving final judgment firmly in human hands.
Behind the scenes, most tools rely on a few core components:
- NLP to assess sentence structure, coherence, tone, and grammar
- Machine learning to detect patterns and ensure consistent grading across submissions
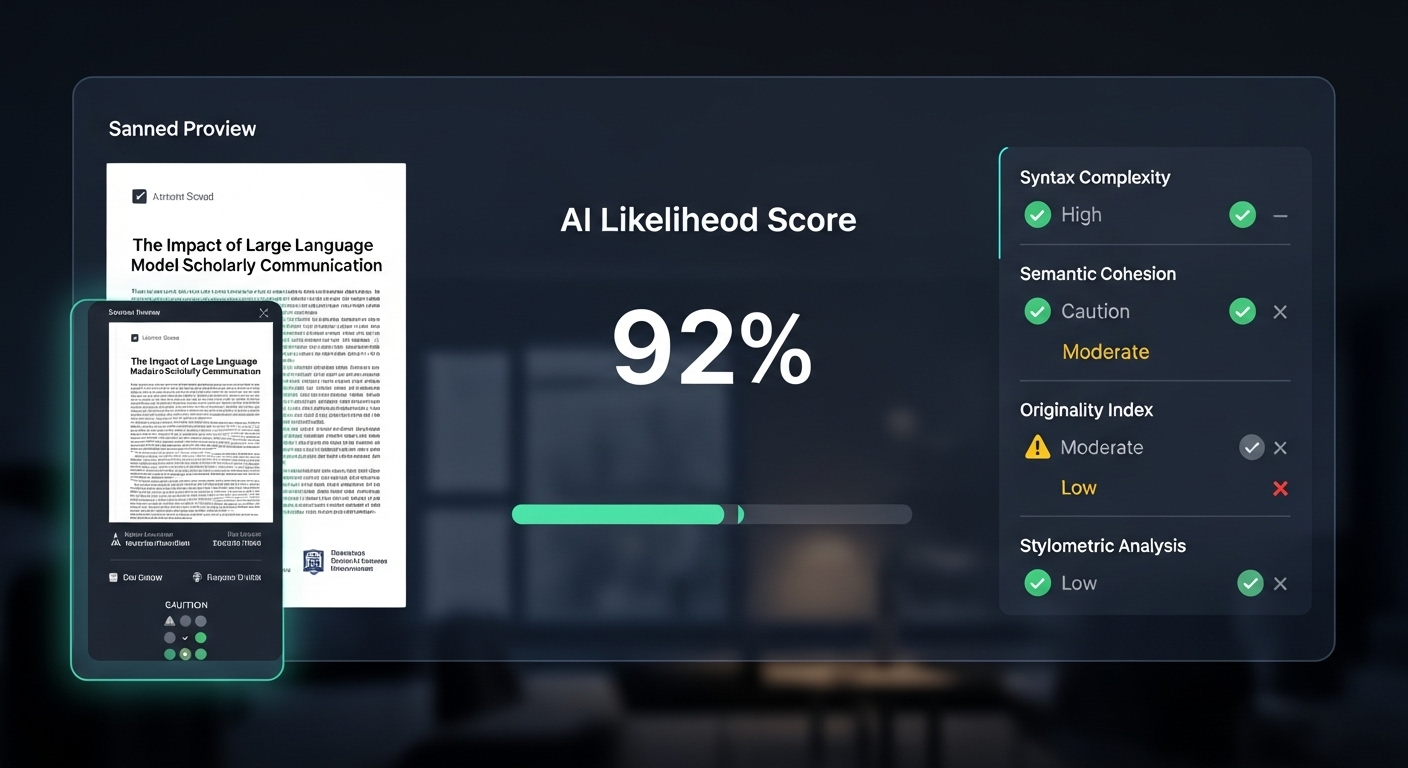
- AI detection tools to flag possible plagiarism or AI-generated content
- LMS integrations with platforms like Google Classroom, Canvas, and Schoology
Think of it less as an autonomous grader and more as a highly organized assistant that never gets tired.
Why Teachers Are Using AI to Grade Essays in the First Place
The appeal isn’t novelty. It’s relief.
Teachers consistently report saving 8–11 hours per week when using AI grading tools, especially during heavy writing cycles. Essays that once took days to return can now receive feedback in minutes. That shift alone changes the rhythm of a course. Students revise while ideas are still fresh. Teachers stop drowning in grading papers.
Consistency is another quiet win. When you’re grading the tenth essay at midnight, fatigue creeps in. AI doesn’t get tired. It applies the same standards across multiple sections and grade levels, reducing unintentional drift and unconscious human bias.
Perhaps the most overlooked benefit is what AI gives back: time. Valuable time. Time for instruction. Time for mentoring. Time for actual feedback conversations instead of just written margins. Used well, AI becomes an incredibly helpful tool not because it replaces judgment, but because it protects it from burnout.
What Parts of Essay Grading AI Handles Well (and What It Doesn’t)

AI essay grading works best when expectations are clear and criteria are defined. That’s where it shines. But it’s not universal, and pretending otherwise creates frustration fast.
AI handles objective elements with impressive consistency. Grammar, syntax, and sentence structure are evaluated quickly and reliably.
Organization, clarity, and alignment with rubric-based grading criteria are also well within its comfort zone. For these areas, AI can provide high-quality, constructive feedback without the variability that human fatigue introduces.
Where AI falls short is just as important.
Creativity, originality, emotional impact, and complex critical thinking still demand human judgment. These are areas where nuance matters, and no algorithm fully understands intent, risk-taking, or voice. That’s not a flaw. It’s a boundary.
In practice, the balance looks like this:
AI handles well
- Grammar, syntax, and structure
- Organization and clarity
- Rubric-aligned criteria
Humans handle best
- Creativity and originality
- Emotional resonance
- Deep, complex thinking
Knowing this division keeps grading fair, efficient, and grounded.
How to Use AI Essay Grading as a “First Pass” (Best-Practice Workflow)
The most effective grading workflows don’t ask AI to decide. They ask it to assist.
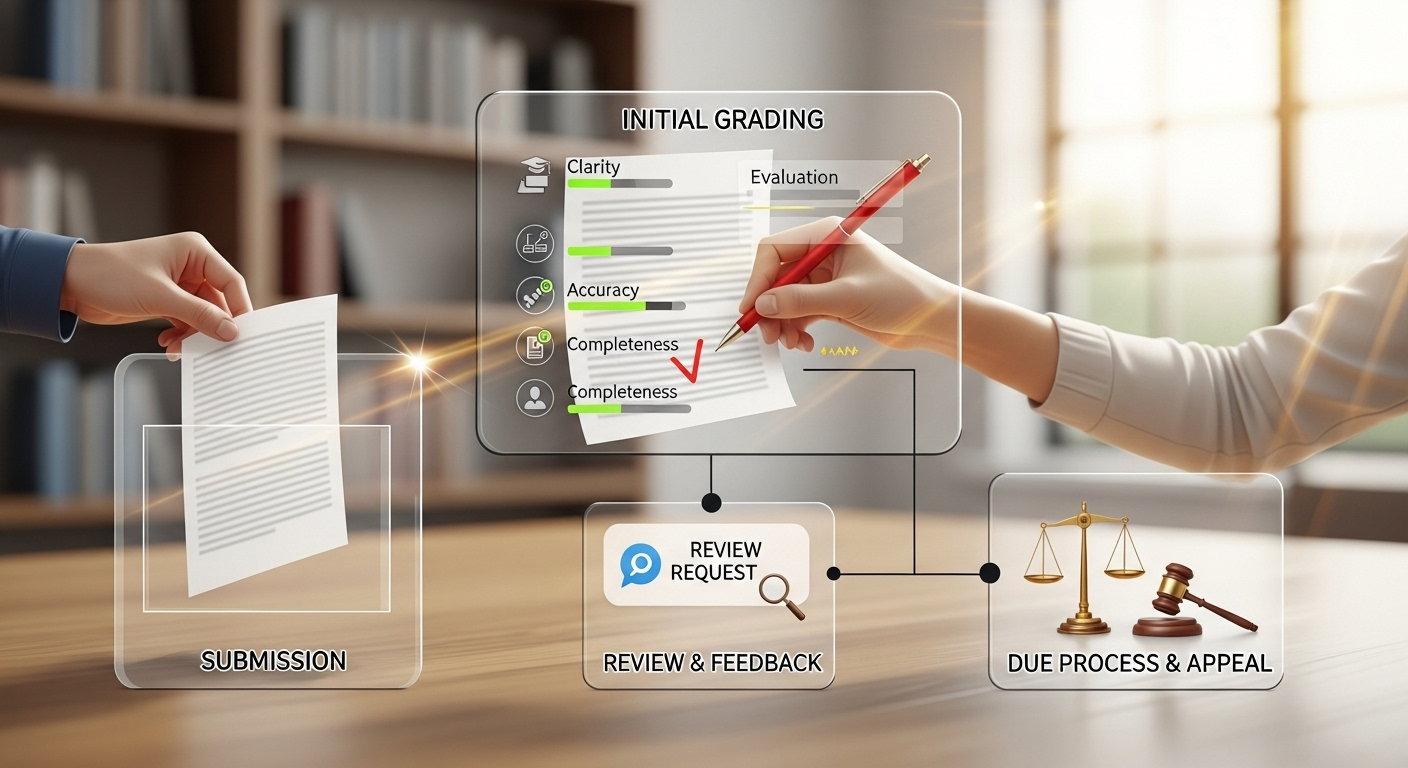
In a first-pass model, AI reviews essays before human evaluation. It flags issues, suggests feedback, and highlights patterns worth attention. From there, you step in. You review. You adjust. You add nuance. You finalize grades. Nothing goes out without your approval.
This hybrid grading process preserves trust on both sides. Students know their work is seen by a human. Instructors maintain full control while benefiting from speed and consistency. Periodic audits of AI feedback help prevent drift, bias, or overreliance, especially as assignments evolve.
Done right, AI grading becomes a reliable results multiplier, not a shortcut. You still double-check. You still decide. The difference is that you’re no longer starting from scratch every time. You’re starting from a well-organized first draft of feedback, and that changes everything.
Can AI Grade Essays Fairly and Consistently Across an Entire Class?

Fairness is usually the first concern, and for good reason. When grading stretches late into the night, even the most careful teacher feels fatigue creeping in. AI helps here by applying the same grading rubric to every student, every time. No drifting standards. No end-of-stack penalty. That alone goes a long way toward ensuring consistent grading across an entire class.
Consistency, though, isn’t the same as neutrality. Bias can still appear, depending on training data and how the tool is configured. That’s why grading standards matter.
When AI evaluates essays against your criteria, not vague benchmarks, inequities are reduced rather than amplified. Patterns become visible, too. If one group of students struggles with the same skill, AI surfaces it without singling anyone out.
Still, AI doesn’t replace judgment. Human review is still required, especially for borderline cases or nuanced writing. The fairest systems combine automation with oversight. AI keeps standards steady across other students. Teachers keep the context, empathy, and discretion that no model can replicate.
What About Academic Integrity, AI Detection, and Plagiarism?
AI grading raises a fair question: if students can use AI to write, how do you protect academic integrity while using AI to grade?
Most AI grading tools include AI detection features that flag potential plagiarism or AI-generated content. These tools don’t accuse. They signal. That distinction matters. Detection should guide review, not trigger automatic penalties.
It’s also important to draw a clear line. Using AI to grade student work is not the same as students using AI to generate essays. One supports evaluation. The other can undermine learning when misused. Transparency helps here. When students know AI is part of the grading workflow, expectations are clearer and trust improves.
Ultimately, academic integrity is preserved through policy and practice, not automation alone. AI flags concerns. Teachers investigate context. Student work is evaluated fairly, with judgment applied where it belongs.
How AI Essay Grading Protects Student Data and Privacy

Student data isn’t a side issue. It’s central.
Responsible AI grading platforms are built to comply with FERPA and GDPR, ensuring student privacy is protected by design, not patched on later. Essays are handled securely, often anonymized during processing so personal identifiers aren’t attached to written assignments.
Most systems limit data collection to what’s necessary for grading. No unnecessary profiles. No harvesting beyond the assignment itself. Access controls and encrypted storage help keep student data secure, whether essays come from Google Classroom or another LMS.
Privacy concerns are valid, especially with new technology. The key is choosing tools that treat data protection as a requirement, not a feature. When handled correctly, AI grading can be both efficient and respectful of student privacy.
How AI Essay Grading Improves Feedback Loops for Students
The biggest shift students notice isn’t automation. It’s speed.
Faster feedback improves writing outcomes because students revise while the work is still fresh. Instead of waiting a week, they receive specific, actionable feedback that points clearly to what worked and what didn’t. That tightens the feedback loop and encourages iteration.
AI grading supports a healthier writing cycle by making revision normal, not exceptional. Students write more because they’re not stuck waiting.
- Instant feedback while learning is fresh, not days later
- Clear “Glow & Grow” insights that balance strengths with next steps
- Stronger revision cycles that reward improvement, not just final drafts
When feedback arrives on time and with clarity, students engage. Writing becomes a process again, not a one-shot performance.
How PowerGrader Helps Teachers Grade Essays With AI—Without Giving Up Control
The difference between a helpful AI grading tool and a risky one comes down to control.
PowerGrader is built around instructor-controlled AI grading. You upload your own rubrics. You tweak criteria. You decide how feedback is delivered. AI supports your workflow rather than redefining it.
Pattern detection helps identify similar responses across an entire class, making it easier to spot trends without flattening individual voices. Because PowerGrader is LMS-ready, it fits into existing systems like Google Classroom and higher education platforms without disruption.
What makes it a game changer isn’t speed alone. It’s the human-in-the-loop design. AI drafts feedback. You refine it. Final judgment stays with you. The grading experience becomes more consistent, more humane, and far less exhausting, without compromising academic integrity or teaching intent.
Is AI Essay Grading a Good Fit for High School and College Classes?
AI essay grading adapts well across contexts, but how it’s used matters.
For high school teachers, AI helps manage large volumes of writing while maintaining consistency across grade levels. It’s especially effective for formative assessments, where timely feedback matters more than final scores.
In college classes, AI scales across sections and supports complex writing tasks without sacrificing standards. It works well for iterative drafts, scaffolded assignments, and feedback-heavy courses.
Across both settings, AI supports multiple levels of writing complexity. What changes is the role of the teacher. AI handles repetition. You handle reasoning, originality, and mentorship.
Conclusion
AI essay grading isn’t about replacing teachers. It’s about protecting them.
Used responsibly, AI becomes a support system that reduces burnout while increasing feedback quality. Human judgment remains the priority.
What changes is the pressure. When time constraints ease, feedback improves. Students write more. Teachers teach better.
The future isn’t fully automated. It’s hybrid. New technology handles the heavy lifting. Humans handle what matters most: meaning, growth, and learning.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is AI essay grading accurate?
AI grading is highly consistent for structure and rubric-based criteria, but accuracy improves most when teachers review and adjust feedback before finalizing grades.
2. Can AI grading be biased?
Bias depends on training data and configuration. Human oversight and periodic review are essential to ensure fair grading outcomes.
3. Is student privacy protected?
Yes. Reputable tools comply with FERPA and GDPR, anonymize submissions, and use secure data handling practices.
4. Does AI replace teacher grading?
No. AI supports grading as a first pass. Teachers retain full control over feedback and final grades.
5. Can AI detect plagiarism or AI-written essays?
Many tools flag potential issues, but detection should guide review rather than automatically penalize students.
6. Is AI grading suitable for creative writing?
AI helps with structure and clarity, but creativity and originality still require human judgment.
7.How long does it take to set up AI grading?
Most tools integrate quickly with LMS platforms, and onboarding typically takes minutes, not weeks.