What is virtual desktop infrastructure? VDI explained
In the past, traditional desktop infrastructure was the primary way for organizations to deploy and manage user workstations. However, with the increase in remote work and the growing demand for secure and flexible access to corporate data, virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) has gained popularity.
Understanding Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI)
Definition and basics of VDI
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) is a virtualization technology that allows a user’s desktop environment to be deployed and managed from a centralized server, rather than being installed and managed on a local device (such as a laptop or desktop computer). This technology enables users to access their desktop environment from any device with an internet connection.
VDI provides a complete desktop environment to the end-user, including an operating system (such as Windows) and the applications required by the user. The backend infrastructure necessary for executing VDI includes a hypervisor (such as VMware or Hyper-V), servers to host virtual machines, and a network connection that allows users to access their virtual desktops remotely.
VDI has become increasingly popular in recent years due to its many benefits, including:
- Centralized management of desktop environments
- Improved security and compliance
- Reduced hardware costs
- Increased flexibility and mobility for end-users
How VDI works: an overview
VDI operates by creating a virtual machine on a central server. The virtual machine includes a complete operating system, applications, and settings required by the end-user. The virtual machine is then remotely accessed by the end-user, typically through a web-based interface or specialized client software that is installed on the user’s local device.
When a user logs in to their virtual desktop, they are presented with a desktop environment that looks and feels like a traditional desktop. However, all of the processing and storage is done on the central server, rather than on the user’s local device. This allows for greater flexibility and mobility, as users can access their desktop environment from any device with an internet connection.
VDI allows IT administrators to manage all desktop environments on a central server, rather than managing multiple individual installations on individual devices. This centralized approach provides IT teams with greater control over desktop environments, enabling them to manage user permissions, security, and settings more efficiently.
Key components of a VDI setup
There are several key components needed for a VDI setup, including:
- Hypervisor: a server that creates and manages virtual machines. The hypervisor is responsible for allocating resources to each virtual machine, ensuring that each virtual machine has the necessary resources to operate efficiently.
- Virtual Desktop Images: a pre-configured virtual machine for each desktop environment. These images are used to create new virtual machines as needed.
- Virtual Machine Manager: software designed to manage virtual machines. This software enables IT administrators to create, delete, and manage virtual machines as needed.
- Thin Clients: low-cost hardware devices that provide remote access to virtual desktops. These devices are typically used in environments where users do not require a full desktop computer.
Overall, VDI is a powerful technology that can provide many benefits to organizations of all sizes. By centralizing desktop environments and enabling remote access, VDI can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and increase flexibility for end-users.
Benefits of implementing VDI
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) is a technology that has been gaining popularity in recent years due to its many benefits. Here are some of the key advantages of implementing VDI:
Enhanced security and data protection
One of the main benefits of VDI is its ability to improve security and data protection. By centralizing data storage, organizations can better control access to sensitive information and limit user permissions. Additionally, VDI offers end-to-end encryption, which adds an extra layer of security to data in transit.VDI also eliminates the need to store data on local devices, which can help organizations comply with data protection regulations and prevent data loss in case of device theft or loss. This can give organizations peace of mind knowing that their data is secure.
Improved resource management and scalability
Another advantage of VDI is its ability to improve resource management and scalability. With VDI, administrators can manage all desktop environments more efficiently and effectively, reducing the overall cost of maintenance and support. In addition, VDI infrastructure can be scaled up or down to match the changing needs of the organization. This makes it a more cost-effective solution in the long-term, as organizations can avoid overprovisioning and only pay for the resources they need.
Cost savings and reduced hardware requirements
VDI can also help organizations save money by eliminating the need to purchase and manage individual workstations. This can result in significant cost savings in the long-term and can also enable organizations to extend the life of existing hardware by using it as a thin client. In addition to reducing hardware expenses, VDI can also help organizations save on energy costs. By centralizing computing resources, organizations can reduce the number of devices that need to be powered on at any given time.
Simplified IT management and maintenance
VDI simplifies IT management and maintenance by centralizing the management of desktop environments. This enables IT administrators to reduce the amount of time and resources required to manage and maintain desktop environments. Additionally, VDI simplifies the deployment of new applications, software updates, and patches. This can help organizations stay up-to-date with the latest software and security updates, which is critical for maintaining a secure and productive computing environment.
Increased flexibility and remote access
Finally, VDI provides users with increased flexibility and remote access. With VDI, users can access their desktop environments securely from anywhere with an internet connection. This enables remote workers to access corporate data and applications without compromising security or productivity. In addition to remote access, VDI can also enable organizations to implement bring your own device (BYOD) policies. This can help organizations attract and retain top talent by allowing employees to use their own devices for work, which can improve job satisfaction and work-life balance. In conclusion, VDI offers many benefits to organizations of all sizes and industries. From enhanced security and data protection to cost savings and increased flexibility, VDI can help organizations improve their computing environments and stay competitive in today’s fast-paced business world.
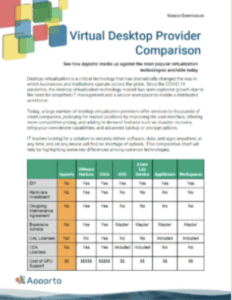
Virtual Desktop Provider Comparison
VDI vs. traditional desktop infrastructure
Comparing performance and user experience
In terms of performance, VDI can offer faster boot times and application load times than traditional desktop infrastructure, provided the infrastructure is designed and optimized correctly. Additionally, because all desktop environments are managed centrally, the end-user experience can be consistent across all users and devices.
VDI can also offer greater flexibility in terms of remote access. With traditional desktop infrastructure, remote access can be difficult to set up and manage, often requiring a VPN connection or other complex network configurations.
Another advantage of VDI is its ability to scale. Traditional desktop infrastructure can be difficult to scale, requiring additional hardware and software licenses to be purchased and installed. With VDI, new virtual desktops can be spun up quickly and easily, allowing organizations to quickly adapt to changing business needs.
Differences in deployment and management
One of the most significant differences between VDI and traditional desktop infrastructure is the centralized management approach taken by VDI. This makes VDI easier to deploy, manage, and support than traditional desktop infrastructure.
With traditional desktop infrastructure, each individual desktop must be managed and maintained separately. This can be time-consuming and can lead to inconsistencies in the end-user experience. With VDI, all desktop environments are managed centrally, making it easier to deploy software updates and patches, manage user accounts, and monitor system performance.
VDI can also offer greater security than traditional desktop infrastructure. With VDI, all data and applications are stored centrally, reducing the risk of data loss or theft. Additionally, because all desktop environments are managed centrally, it is easier to enforce security policies and monitor user activity.
Evaluating costs and return on investment
VDI can require a significant upfront investment in infrastructure and hardware. However, over time, the cost savings and greater efficiency enabled by VDI can result in a positive return on investment (ROI).
One of the key cost savings associated with VDI is the reduced need for hardware. With traditional desktop infrastructure, each individual desktop requires its own hardware, including a CPU, hard drive, and memory. With VDI, multiple virtual desktops can be run on a single physical server, reducing the need for additional hardware.
VDI can also offer greater energy efficiency than traditional desktop infrastructure. Because multiple virtual desktops can be run on a single physical server, VDI can reduce the amount of energy required to power and cool data centers.
Finally, VDI can offer greater productivity and efficiency than traditional desktop infrastructure. With VDI, employees can access their desktops from anywhere with an internet connection, allowing them to work from home or on the go. Additionally, because all desktop environments are managed centrally, it is easier to deploy new applications and updates, reducing downtime and increasing productivity.
Types of VDI deployments
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) is a technology that enables organizations to host desktop environments on a centralized server and provide access to them remotely. There are different types of VDI deployments that organizations can choose from based on their needs and requirements.
Persistent vs. non-persistent VDI
Persistent VDI maintains a persistent virtual machine for each user, ensuring that individual customizations and settings are saved across sessions. This means that users can log in and find their desktop environment exactly as they left it, with all their files, applications, and settings intact. This type of VDI is ideal for users who require a high degree of customization and personalization, such as developers, designers, and power users.
In contrast, non-persistent VDI creates a new virtual machine image for each session, eliminating the need for storage of individual user settings. This type of VDI is ideal for users who require a standardized desktop environment, such as call center agents, customer service representatives, and other knowledge workers.
Cloud-based vs. on-premises VDI
A cloud-based VDI is hosted in the cloud and accessed remotely by end-users. This type of VDI offers several advantages, such as reduced hardware and maintenance costs, greater scalability, and easier access for remote workers. Cloud-based VDI can also be deployed quickly, which makes it ideal for organizations that need to set up new desktop environments quickly.
An on-premises VDI is hosted on local servers and accessed over the organization’s internal network. This type of VDI offers greater control and security, as the organization has complete control over the infrastructure. On-premises VDI is also ideal for organizations that need to comply with strict data privacy regulations or have specific hardware requirements.
Hybrid VDI solutions
A hybrid VDI solution combines both cloud-based and on-premises VDI solutions to provide greater flexibility and scalability. This type of VDI is ideal for organizations that need to manage fluctuating demand for desktop environments. For example, during peak periods, the organization can use cloud-based VDI to quickly spin up new desktop environments, while during off-peak periods, the organization can use on-premises VDI to save costs.
Hybrid VDI solutions can also be used to provide redundancy and disaster recovery. In case of a hardware failure or a natural disaster, the organization can quickly switch to the other VDI solution to ensure business continuity.
Conclusion
Virtual desktop infrastructure offers organizations greater flexibility and control over their desktop environments, enabling remote work, improving security, and reducing costs. Choosing the right approach requires an understanding of the organization’s needs, infrastructure, and resources, as well as careful consideration of the costs and benefits associated with each option.
Check out this related article on other desktop virtualization solutions and how to choose the right provider.