Simplifying IT Management with Virtual Desktops: Key Considerations for IT Professionals
The rapid advances in technology over the last few decades have revolutionized the way businesses operate. Companies around the world are racing to adopt technology solutions that can keep them competitive and agile in the marketplace. At the same time, managing the complexity of IT systems has become a major headache for IT professionals. One approach that has gained popularity in recent years is virtual desktops. Virtual desktops offer significant benefits to organizations looking to streamline IT management. In this article, we will explore the key considerations that IT professionals should weigh before implementing virtual desktops in their organizations.
Understanding Virtual Desktops and Their Benefits
Virtual desktops is a technology that allows users to access a centralized desktop environment from anywhere in the world using any device. In other words, virtual desktops put all the apps, programs, and files in one place on a remote server. Instead of having to install software and store files on a local device, users can access their desktops from a remote server using a client application. Virtual desktops offer several benefits over traditional desktops, including:
- Reduced hardware costs
- Minimized overhead of managing lots of separate systems
- Better security
- Reduced energy costs and carbon footprint
Let’s dive deeper into what virtual desktops are and how they can benefit your organization.
What are Virtual Desktops?
Virtual desktops are essentially a remote desktop environment that is stored on a server. Instead of having to install software and store files on a local device, users can access their desktops from a remote server using a client application. This is called a virtual machine. Each virtual desktop is isolated from others, so users can customize their settings and install and run the applications they need without worrying about affecting other users. This means that users can work from anywhere, at any time, using any device, and still have access to all of their applications and files.
Virtual desktops can be accessed through a variety of devices, including desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones. This makes it easy for users to work from home, on the go, or in the office without having to worry about carrying around a heavy laptop or desktop computer.
Advantages of Implementing Virtual Desktops
Implementing virtual desktops has several advantages. First, they reduce hardware costs because you don’t need to purchase high-powered, expensive desktops or laptops. Instead, you can use less expensive thin clients or repurpose older hardware. Second, they minimize the overhead of managing lots of separate systems. With virtual desktops, IT administrators can manage all desktops from a central location, which reduces the need for onsite support and maintenance. Third, they offer better security because all data is stored centrally and can be backed up easily. This means that if a device is lost or stolen, the data is not lost. Lastly, virtual desktops reduce energy costs and carbon footprint because less power is consumed by desktops and servers.
Virtual desktops also offer a better end-user experience by providing a consistent environment across devices and locations and enabling support for Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies. With virtual desktops, users can work from any device and still have access to all of their applications and files.
How Virtual Desktops Simplify IT Management
Virtual desktops offer IT professionals a scalable, manageable, and secure solution to manage the complexity of IT infrastructure. Virtual desktops allow administrators to deploy, manage, maintain, and update desktop environments centrally, without having to worry about individual desktops. This means that IT administrators can focus on more strategic projects instead of spending time on routine maintenance and support tasks.
Virtual desktops offer a lower total cost of ownership (TCO) due to reduced hardware costs, maintenance, and support. With virtual desktops, IT administrators can easily deploy new desktops, update software, and manage security patches from a central location. This reduces the need for onsite support and maintenance, which can save organizations money in the long run.
In conclusion, virtual desktops offer several benefits over traditional desktops, including reduced hardware costs, better security, and simplified IT management. If you’re looking for a scalable, manageable, and secure solution for your organization, virtual desktops may be the answer.
Assessing Your Organization’s Needs
The decision to implement virtual desktops should be based on a thorough assessment of the organization’s needs and goals. IT professionals need to evaluate their current infrastructure, identify key business requirements, and estimate the cost of implementation. This assessment should cover the following factors:
Evaluating Current IT Infrastructure
The first step in assessing your organization’s needs is to evaluate your existing IT infrastructure. This step will help you identify areas that need improvement, understand the current resources, and determine whether your infrastructure can support a virtual desktop environment. Key factors to consider include the size of your organization, the number of users, the types of applications used, and the hardware and software currently in use.
For example, if your organization has a large number of users who require access to high-performance applications, you may need to invest in more powerful servers or storage solutions to support a virtual desktop environment. On the other hand, if your organization has a smaller number of users who primarily use basic office applications, your existing infrastructure may be sufficient to support virtual desktops.
Alternatively, many organizations are now turning towards a Desktop-as-a-Service (DaaS) as it allows them to offload the management of the infrastructure and dramatically reduce costs.
Identifying Key Business Requirements
Before selecting a virtual desktop solution, you need to identify the business requirements that are driving your need for virtual desktops. This might include remote access, mobility, security, compliance, disaster recovery, or other factors. Understanding these requirements will help you determine the features and capabilities you need from a virtual desktop solution.
For example, if your organization has a large number of remote workers who need access to desktop applications, you may need a virtual desktop solution that provides secure remote access. Alternatively, if your organization operates in a highly regulated industry, you may need a virtual desktop solution that meets specific compliance requirements.
Estimating the Cost of Implementation
The cost of implementing virtual desktops will depend on a variety of factors, including the size of your organization, the number of desktops, the complexity of your environment, and the features and capabilities you need. You will need to evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO) of virtual desktops, including licensing, hardware, storage, bandwidth, and ongoing support and maintenance costs. It is critical to gain a thorough understanding of the costs involved before making a decision.
For example, if your organization has a large number of desktops that require high-performance hardware, the cost of implementing virtual desktops may be higher than if you have a smaller number of desktops that require less powerful hardware. Additionally, ongoing support and maintenance costs can vary depending on the complexity of your environment and the level of support required.
Overall, a thorough assessment of your organization’s needs is critical to the success of a virtual desktop implementation. By evaluating your current infrastructure, identifying key business requirements, and estimating the cost of implementation, you can make an informed decision about whether virtual desktops are the right solution for your organization.
Choosing the Right Virtual Desktop Solution
Choosing the right virtual desktop solution is critical to the success of your implementation. There are many virtual desktop providers in the market, and it can be challenging to navigate the options available. IT professionals need to consider several factors when selecting a virtual desktop provider, including:
- Experience
- Reliability
- Scalability
- Security
- Implementation Effort
- Support
When assessing virtual desktop providers, consider these factors carefully. Look for providers that have a proven track record of delivering high-quality, secure, and reliable services to their customers. Evaluate the providers’ ability to scale their solutions to accommodate your organization’s growth and future requirements, including the ability to integrate with your existing IT infrastructure.
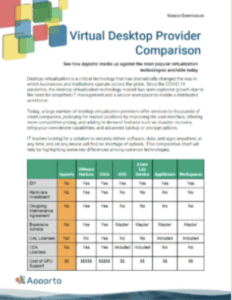
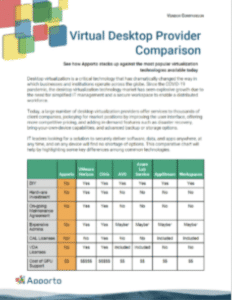
Comparing Virtual Desktop Providers
Comparing virtual desktop providers can be a daunting task, but it is essential to make an informed decision. Start by researching the providers’ backgrounds and reputation in the industry. Consider the provider’s experience in delivering virtual desktop solutions, the size of their customer base, and the industries they serve. Look for customer reviews and case studies to gain insight into the provider’s performance and customer satisfaction.
By comparing the providers’ offerings against these criteria, you can make an informed decision that will meet your organization’s needs.
Virtual Desktop Provider Comparison
Key Features to Look for in a Solution
When comparing virtual desktop solutions, look for features that will enhance the end-user experience and provide the functionality and flexibility that your organization requires. Some of the key features to consider include:
- Support for multiple devices
- Mobility
- Security
- Client-less remote access
- Integrations
- Customization options
- High availability
- Disaster recovery
- OS support
By evaluating these features, you can ensure that your virtual desktop solution meets your organization’s needs and provides a seamless end-user experience.
Ensuring Scalability and Flexibility
Your virtual desktop solution must be able to handle the growth of your organization and adapt to changing requirements. Evaluate the scalability and flexibility of the providers’ solutions, including the ability to support remote and mobile users, support Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies, and integrate with your existing infrastructure seamlessly.
Consider the provider’s ability to deliver a solution that can scale up or down as your organization’s needs change. Look for providers that offer flexible pricing models, so you only pay for what you need. By ensuring scalability and flexibility, you can future-proof your virtual desktop solution and ensure that it meets your organization’s needs for years to come.
Implementing Virtual Desktops in Your Organization
Once you have assessed your needs, selected the right virtual desktop solution, and estimated the cost of implementation, it’s time to deploy virtual desktops in your organization. Deploying virtual desktops requires careful planning, preparation, and execution. Key factors to consider include:
Preparing Your IT Infrastructure
Before deploying virtual desktops, you need to prepare your IT infrastructure to ensure that it is stable, secure, and scalable to accommodate the new environment. This might include upgrading your network infrastructure, adding additional servers, installing new security measures, or updating your software. You will also need to allocate sufficient resources to support your users, including bandwidth, storage, and support personnel.
Alternatively, if you are going the DaaS route then much of the infrastructure planning can be skipped.
Training Your IT Team and End Users
Virtual desktops require a different set of skills and knowledge than traditional desktops. Your IT team and end-users will need to be trained to use the new environment. Training should cover topics such as accessing the virtual desktop, managing files, installing applications, and troubleshooting common issues. Training should be ongoing to ensure that your users are using the virtual desktop environment efficiently and securely.
Monitoring and Managing the Virtual Desktop Environment
Once your virtual desktop environment is deployed, you will need to manage and monitor it carefully to ensure that it is performing as expected. You will need to monitor performance, troubleshoot issues, and update software on a regular basis to keep the environment secure and stable. You will also need to manage end-users’ access to the virtual desktop environment to ensure that sensitive data is protected.
For cloud based models, much o the monitoring in maintenance is handled by the provider. For more information on cloud based desktops aka DaaS, learn more here.
Conclusion
Virtual desktops can offer IT professionals a powerful way to simplify IT management, reduce costs, improve security, and enhance the end-user experience. However, to reap the benefits of virtual desktops, you need to carefully assess your organization’s needs, choose the right virtual desktop solution, and implement it in a thoughtful and strategic manner. By following the key considerations outlined in this article, you can ensure that your organization is well-positioned to take full advantage of the benefits of virtual desktops.