Introduction
University and college computer labs have undergone a remarkable evolution that mirrors the advancement of technology and its impact on education. From their early days as mainframe sanctuaries to their current role as digitally connected hubs, these labs have played a significant role in shaping students’ technological literacy. This blog post delves into the rich history, transformative journey, and future prospects of computer labs on university and college campuses.
The Early Years: Tracing the Genesis of Technological Access
In the mid-20th century, the emergence of computer labs marked a significant milestone as universities gained access to mainframe computers. These labs initially catered to computer science and engineering students, offering hands-on experience with computing power that was otherwise inaccessible. The massive mainframes, often requiring dedicated rooms for installation, were managed by specialized personnel. Students would write programs on punch cards, submit them for processing, and eagerly await results, showcasing a stark contrast to the immediacy of today’s digital landscape.
Read More: ‘Hidden Figures’ by Margot Lee Shetterly
The Rise of Personal Computing: Shaping a New Paradigm
The 1980s marked a transformative era for university computer labs, as the introduction of personal computers ignited a seismic shift in their role and significance. This period witnessed a revolution in technology that would redefine the way students interacted with computers and set the stage for the digital landscape we know today.
Empowering Student-Centered Learning
Personal computers, with their compact design and user-friendly interfaces, democratized access to computing resources. University computer labs underwent a metamorphosis, expanding their reach beyond the realm of computer science and engineering departments. Suddenly, disciplines across the academic spectrum could harness the power of computing to enhance their learning experiences.
For instance, art and design students found newfound avenues for creativity through graphic design software, allowing them to experiment with digital artistry and manipulate visuals in ways previously unimaginable. Economics students leveraged spreadsheet software to analyze complex data sets, enabling them to develop a deeper understanding of economic trends and theories. Language and literature students delved into word processing, revolutionizing the way they wrote and edited essays, dissertations, and creative works.
Facilitating Collaborative Endeavors
The rise of personal computing within university computer labs also fostered a spirit of collaboration among students. Software applications for communication and project management began to emerge, empowering students to work together on assignments and projects regardless of their physical locations. This newfound connectivity transcended geographical boundaries, enabling cross-disciplinary teamwork and information sharing.
For instance, a group of engineering and business students could collaborate on a prototype for a sustainable energy solution using specialized design software and then present their findings using multimedia presentation tools. Similarly, biology and computer science students might collaborate on computational modeling projects to simulate complex biological processes, enhancing their collective understanding of intricate biological phenomena.
Cultivating Technological Literacy
Personal computers not only reshaped the dynamics of university computer labs but also played a pivotal role in fostering technological literacy among students. As these labs expanded their offerings, students from diverse backgrounds gained proficiency in using a range of software applications, hardware components, and digital tools. This fluency not only enhanced their academic pursuits but also equipped them with practical skills that were increasingly valued in the job market.
For instance, a sociology major might become adept at data visualization tools, enabling them to transform sociological trends into compelling visual narratives. A music student could explore music production software, composing and arranging intricate pieces that blend traditional musical elements with cutting-edge technology. These skills, cultivated within the university computer lab environment, would go on to enrich students’ professional journeys across various industries.
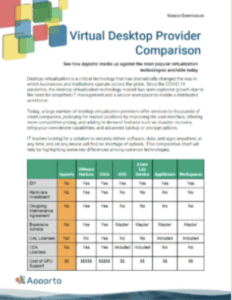
Virtual Computer Labs: 2-year Impact Assessment Conducted by IIT

The Internet Revolution and Beyond: Shaping Modern Campus Dynamics
The turn of the millennium ushered in the internet revolution, propelling university computer labs into a new era. Internet connectivity became a standard offering, enabling students to access online research, communication tools, and collaborative platforms. The modern computer lab experience embraced e-learning platforms, digital libraries, and online collaboration spaces, empowering a generation of digitally fluent learners.
[Webinar] Educause CIO Panel Discussion – The Future of Computer Labs
Mobile Technology and Beyond: Adapting to a Changing Landscape
In today’s mobile-centric world, university computer labs are once again at a crossroads. With the prevalence of laptops, tablets, and smartphones, the traditional concept of a centralized physical lab is evolving. Many institutions are embracing a “bring your own device” (BYOD) approach, providing Wi-Fi-equipped communal spaces for study and collaboration. However, this shift prompts a reevaluation of the traditional computer lab’s role.
The Future Vision: Redefining University Computer Labs
While the physical configuration of computer labs may change, their significance remains undiminished. The future envisions computer labs as adaptable spaces that cater to evolving learning needs. Here are some exciting possibilities:
- Cutting-edge Cloud-based Labs: As emerging technologies like AI, virtual reality, and quantum computing gain prominence across disciplines, cloud-based labs enable students to learn from any location and can provide immersive learning experiences and experimentation opportunities.
- Innovation Ecosystems: University computer labs could transform into innovation ecosystems, facilitating interdisciplinary collaboration and encouraging students to tackle real-world challenges using technology-driven solutions. This scenario can be further extended to cloud-based labs with integrated collaboration features.
- Empowering Makerspaces: Equipped with advanced tools such as 3D printers and robotics kits, future computer labs might become dynamic maker spaces, fostering hands-on exploration and creativity.
- Digital Wellness Centers: Recognizing the need for digital well-being, computer labs could incorporate resources and workshops that promote healthy technology usage and help students strike a balance between their digital and offline lives.
Conclusion
The evolution of university and college computer labs serves as a testament to the symbiotic relationship between technology and education. From their early roots as mainframe havens to their current role as dynamic hubs, these labs have consistently adapted to meet the changing needs of students. As we peer into the future, the metamorphosis of computer labs continues, driven by the transformative potential of emerging technologies and the ongoing mission of preparing students for a tech-centric world. Whether through specialized labs, innovation ecosystems, or other innovative models, one thing remains certain: the journey of university computer labs is an ever-evolving saga with exciting chapters yet to be written.