In today’s digital world, businesses are increasingly relying on cloud-based solutions to streamline operations and enhance collaboration. Two such technologies that are gaining popularity are cloud desktops and virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI). While both of these solutions serve similar purposes, they differ in several key ways. In this article, we will explore the differences between cloud desktops and VDI, and help you decide which technology is the best choice for your organization.
What is VDI?
Virtual desktop infrastructure, or VDI, is a solution that enables users to access remote desktops from any device with an internet connection. With VDI, the desktop environment is virtualized and run on servers in a data center. Users can connect to their virtual desktops through thin clients or other devices, and access their applications, data, and files as if they were using a traditional desktop computer.
VDI has several benefits, such as improved security, centralized management, and reduced hardware costs. Since the desktop environment is hosted on centralized servers, IT teams can easily manage and update all virtual desktops in the data center. This also means that sensitive data and applications are kept secure in the data center, rather than being stored on local devices.
One of the biggest advantages of VDI is its ability to provide a consistent user experience across different devices. With VDI, users can access their virtual desktops and applications from anywhere, on any device, without having to worry about compatibility issues. This is particularly useful for organizations with a mobile workforce, as it allows employees to work remotely without sacrificing productivity or security.
VDI can also help organizations reduce their hardware costs. Since the desktop environment is hosted on centralized servers, users do not require powerful local devices to run their applications. This means that organizations can save money by purchasing less expensive thin clients or repurposing older devices as VDI endpoints.
In conclusion, VDI is a powerful solution that can help organizations improve their security, reduce costs, and provide a consistent user experience across different devices. By virtualizing the desktop environment and hosting it on centralized servers, VDI enables users to access their applications and data from anywhere, on any device, while keeping sensitive information secure in the data center.
What are Cloud Desktops?
Cloud desktops are a relatively new technology that allows users to access their desktop environments remotely. This means that users can access their files, applications, and settings from anywhere in the world, as long as they have an internet connection.
Cloud desktops are similar to virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) in that they both allow users to access desktop environments remotely. However, there are some key differences between the two technologies.
One of the main differences between cloud desktops and VDI is where the hosting infrastructure is located. With VDI, the hosting infrastructure is typically located in a company’s data center. This means that businesses need to invest in costly hardware and IT resources to set up and maintain the infrastructure.
Cloud desktops, on the other hand, are hosted in the cloud. This means that businesses don’t need to invest in hardware or IT resources to set up and maintain the infrastructure. Instead, they can rely on a third-party provider to handle the management and maintenance of the infrastructure.
Another key difference between cloud desktops and VDI is scalability. With VDI, businesses need to plan for their future needs and invest in hardware and IT resources accordingly. This can be costly and time-consuming, especially if the business experiences unexpected growth or changes in demand.
Cloud desktops, on the other hand, offer businesses the flexibility and scalability they need to adapt to changing requirements. Since the hosting infrastructure is provided by a third-party provider, businesses can easily scale up or down as needed, based on their changing requirements.
Overall, cloud desktops are becoming increasingly popular among organizations of all sizes. They offer a cost-effective and flexible solution for remote access to desktop environments, without the need for significant investments in hardware or IT resources associated with VDI.
Cloud Desktops vs. VDI: Key Differences
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) and cloud desktops are two popular solutions for businesses to provide their employees with remote access to their desktops. While they share many similarities, they differ in several key areas, which are discussed below.One of the main differences between VDI and cloud desktops is the location of the hosting infrastructure. VDI infrastructure is typically located in a company’s own data center, which means that the company has complete control over the infrastructure and can customize it to their specific needs. This level of control also means that the company is responsible for managing and maintaining the infrastructure, which can be expensive and time-consuming. Cloud desktops, on the other hand, are hosted in the cloud, which means that the infrastructure is managed by a third-party provider. This can be a cost-effective solution for businesses that do not have the resources to manage their own infrastructure.
Another key difference between VDI and cloud desktops is the level of control and customization that businesses have over their desktop environments. With VDI, businesses have complete control over the desktop environment and can customize it to their specific needs. However, this level of control also means that the business is responsible for managing and maintaining the desktop environment. This can be a time-consuming and expensive process, especially for businesses with a large number of desktops. Cloud desktops, on the other hand, may offer less control over the desktop environment, though this varies by provider. Businesses can choose from a range of pre-configured desktop environments, but they may not customize them to the same extent as with VDI. Again, this varies by provider and may not be true in all cases. However, this also means that the business is not responsible for managing and maintaining the desktop environment, which can be a significant cost savings.
In addition to these key differences, there are several other factors that businesses should consider when choosing between VDI and cloud desktops. These include the cost of the infrastructure, the level of security that is required, and the scalability of the solution. Ultimately, the choice between VDI and cloud desktops will depend on the specific needs and requirements of each organization.
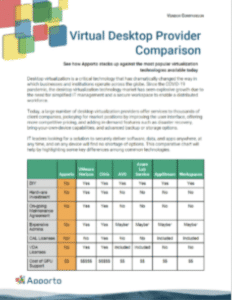
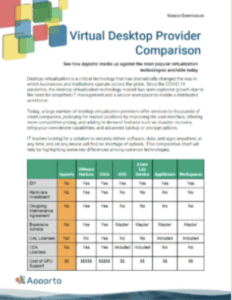
Cloud Desktop Provider Comparison
Understanding the Benefits of Cloud Desktops and VDI
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) and cloud desktops are two popular solutions that businesses use to provide their employees with remote access to their desktop environments and applications. Both VDI and cloud desktops offer businesses a range of benefits that can help improve productivity, collaboration, and security.
Benefits of VDI
One of the biggest advantages of VDI is centralized management. With VDI, businesses can manage and update all virtual desktops in the data center, which can save IT teams time and resources over non-virtualized solutions.
VDI also offers improved security. Since the desktop environment is hosted in the data center, sensitive data and applications are kept secure. This is particularly important for businesses that deal with sensitive information, such as financial institutions or healthcare organizations. With VDI, businesses can ensure that their data is protected from unauthorized access or theft.
Another benefit of VDI is reduced hardware costs. Since all desktop environments are hosted in the data center, businesses can reduce their investment in hardware. This means that businesses can save money on hardware costs and reduce their environmental impact by using fewer resources.
Benefits of Cloud Desktops
Cloud desktops offer businesses greater flexibility and scalability. With cloud desktops, businesses can easily scale up or down as needed, based on their changing requirements. This means that businesses can quickly adapt to changes in demand and avoid the costs associated with over-provisioning or under-provisioning hardware.
Additionally, since the hosting infrastructure is provided by a third-party provider, businesses can reduce their investment in hardware and IT resources. This means that businesses can focus on their core competencies and leave the management of the hosting infrastructure to the experts.
Cloud desktops also offer businesses greater accessibility. Since cloud desktops can be accessed from any device with an internet connection, employees can work from anywhere, at any time. This can improve productivity and collaboration, as employees can easily collaborate with colleagues and access their work from any location.
What Are the Limitations of Cloud Desktops & VDI?
While both VDI and cloud desktops offer businesses a range of benefits, there are also some limitations to consider. With VDI, businesses must invest in expensive hardware and IT resources to manage and maintain the infrastructure. Additionally, if there are any issues with the data center or network, users may experience disruptions or downtime, leading to lost productivity.
Cloud desktops also have limitations, such as reduced customization and control over the environment. Since the hosting infrastructure is managed by a third-party provider, businesses may have less control over the environment and could be limited in the customizations they can make. Additionally, if there are any issues with the provider’s infrastructure or network, users may experience disruptions or downtime.
Comparing Costs: Cloud Desktops vs VDI
When it comes to costs, there are some key differences between VDI and cloud desktops. With VDI, businesses typically have to invest in expensive hardware and IT resources to set up and manage the infrastructure. This can be a significant upfront cost for many organizations.
With cloud desktops, on the other hand, businesses typically pay a monthly or annual subscription fee to the provider. While this fee can add up over time, it is often less expensive than the upfront costs of VDI. Additionally, since the provider manages and maintains the infrastructure, businesses can avoid many of the ongoing costs associated with managing their own data center.
Conclusion
Both cloud desktops and VDI offer businesses the ability to enable remote work and improve productivity and collaboration. While they share many similarities, they also differ in several key areas, such as the location of the hosting infrastructure and levels of control and customization. When deciding between these solutions, businesses should consider their specific needs, such as scalability, control, and costs, to determine which technology is the best choice for their organization.